Introduction
A router is a box that allows multiple computers, smartphones, and so on to join the same network. From there, the router is typically connected to a modem in order to provide an Internet connection to any device that is connected to the router. This guide aims to help you through the first-time setup process for your router.
In the box you may have some of the following:
The router’s power supply or charger.
Device manual.
Driver disc (for some models).
USB cable (for some models).
Network cable (for some models).
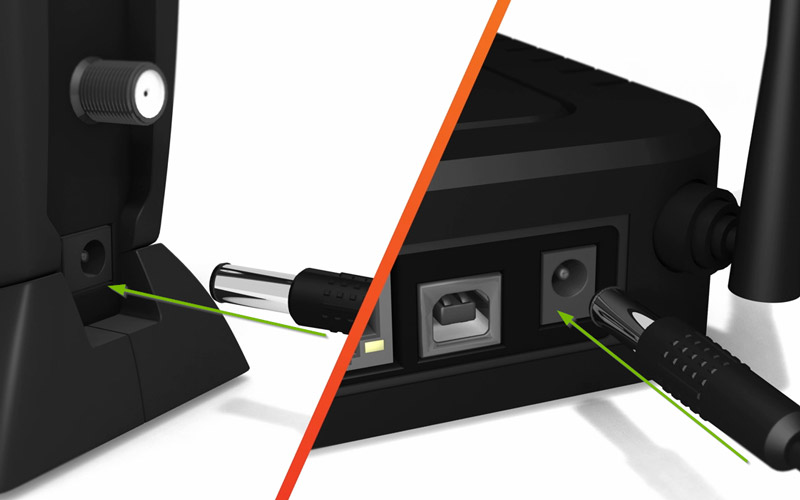
1 Connect Power
Please ensure that you are using the power adapter that came with your router.
Locate the power cable and connect it to a power source like an outlet or surge protector.
Plug the other end of the power cable to the router’s power input, which is typically located in the rear.
Your router should power on.
2 Connect to Modem by Cable/Wire
Your router must be connected to a modem so as to provide the local network with an Internet connection.
Acquire an Ethernet cable.
Take one end of the cable and plug it into the Internet (or WAN) port on the rear of your router. The port may be blue or grey.
Take one end of the cable and plug it into an available Ethernet (or LAN) port on the rear of your modem. These ports are typically yellow.
Usually this is all that is needed to connect your router to a wired connection.
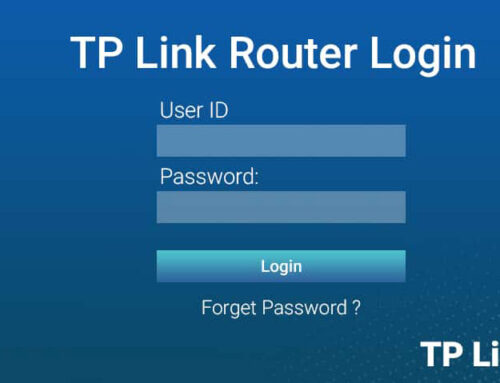
3 Log In
Using a computer that is connected to the TP-Link router, open a web browser (for example, Safari, Google Chrome or Internet Explorer).
At the top of the browser is the address bar, type in http://tplinkwifi.net.
If the address does not work, check the bottom of the router to confirm the default access address. You can also try to connect via IP address (example: http://192.168.1.1 or http://10.0.0.1).
You may find it on the same label where your router’s address is if you are prompted for a username and password.
The default credentials are typical:.
Username: admin.
Password: admin.
4 Select Password.
Wherever possible, you should pick a password that is impossible to guess and is also resistant to brute-force attacks.
Some devices or systems do not allow special characters or they may have their own requirements.
Password Dos and Do n’ts.
Dos.
Passwords should be long, 8-12 characters or more.
Passwords should be something easy for you to keep in mind, but hard for others to guess or lookup.
Passwords should have lots of different character types: upper and lower case symbols, letters, and numbers.
Replacing letters with symbols is a simple way to achieve this: use @ for a, and (for c, as example.
Passwords are personal, most services have a way to create a ‘linked’ account or share services with trusted friends and family.
Change passwords regularly. Every 90 to 180 days; this helps keep your accounts from being compromised long-term.
If you must write down a password or make note of it, do so only in specially designed programs, or keep and hold the physical copies with the same care and respect you would a social security card or birth certificate. Remember; anyone with your password “is you”.
Example of a good password.
Don’ts.
Don’t use short passwords; computers can guess them very easily.
Don’t use a common word you can find in a dictionary.
Don’t use information that can be looked up or guessed, such as a birthday, pet, or anniversary ‘s name.
Don’t use the same password for everything. All of the same ones are compromised across all your accounts if one password is compromised.
Don’t share passwords. People with your password “are you” to a computer system, or a service.
Don’t keep the same password forever. Assume that, at some point, it will be guessed, seen, or otherwise compromised, and it must be changed.
Don’t write down passwords in the open, or save them in non-encrypted files on your computer.
5 Change SSID and Password.
After logging-in the router’s user interface:
Click on Wireless 2.4 then Wireless Settings.
Confirm or change the Network Name. When searching for available wireless networks in the area, the network name (or SSID) is the name others will see.
Next, click on Wireless Security and type your new password. Scroll down and click Save.
For Version, select WPA2-PSK.
One some models you must select the Security and then the Version. Choose WPA/WPA2 – Personal and WPA2-PSK.
Enter the password you have chosen in the box next to Password.
Once complete, click Save.
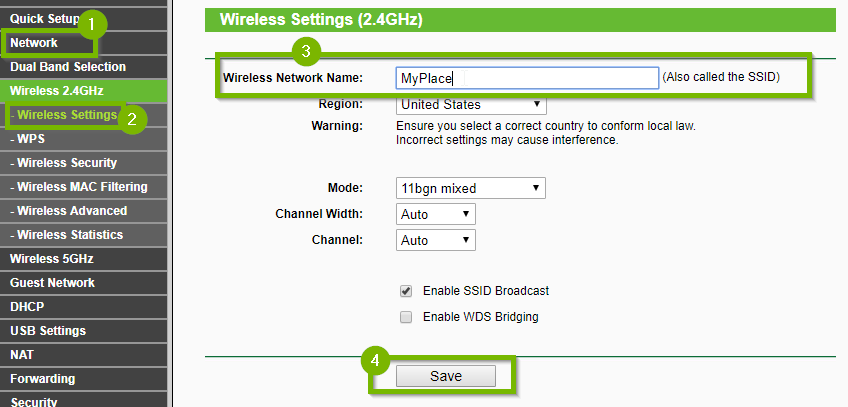
Your wireless security settings have now been updated and your devices may connect to it.
Any time you change your wireless security settings you will need to reconnect your wireless devices.
If your router is dual-band, meaning it has a 2.4 and a 5 GHz network you may need to repeat the steps listed above for each network because each network may be controlled individually. You must use different network names for each band.
Because it is controlled separately, if your router has a guest network you will need to repeat the steps listed above for the guest network.
6 Keeping Your Password Secure.
Some precautions should be taken in order to keep your password secure.
Best practices:.
Do not use a master password that you use everywhere (like email, work, school, home, network).
Do not share your password with anybody if possible.
Passwords that are shared with others, like for a home network, should only be shared if necessary.
Be aware when typing your password in public, or that in no way anyone is watching.
Some types of electronic devices like smartphones and computers can remember passwords, so beware of devices that are not yours.
When to change your password, make a schedule of. As an example, every 180 days.
It is not recommended to write down passwords. But if you have to, ensure that it is neither physically nor visually accessible by others.
7 Deciding to Update.
Router updates are provided to add new security features, fix vulnerabilities, or other enhancements like performance upgrades. We recommend updating your router at this time so as to get the best possible security. Depending upon the model, you may need an internet connection, access to a computer, and a formatted USB flash drive in order to update.



Leave A Comment